RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) integration
RAG helps your AI agent find relevant information from documents to give better answers. It searches through your knowledge base and uses that context to respond more accurately.
Architecture
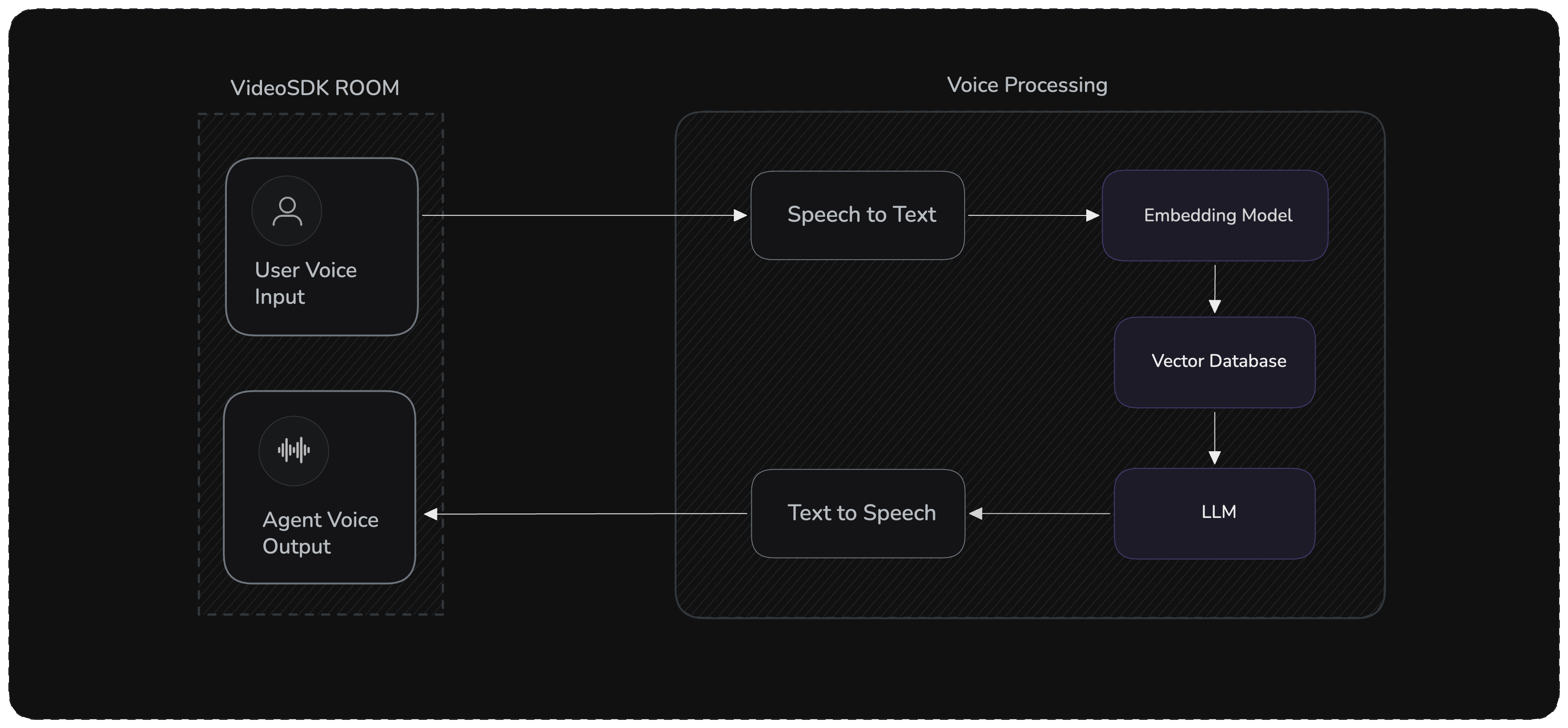
The RAG pipeline flow:
- Voice Input → Deepgram STT converts speech to text
- Retrieval → Query embeddings fetch relevant documents from ChromaDB
- Augmentation → Retrieved context is injected into the prompt
- Generation → OpenAI LLM generates a grounded response
- Voice Output → ElevenLabs TTS converts response to speech
Prerequisites
-
Install VideoSDK agents with all dependencies:
pip install "videosdk-agents[deepgram,openai,elevenlabs,silero,turn_detector]"
pip install chromadb openai numpy -
Set API keys in envrionment:
.envDEEPGRAM_API_KEY = "Your Deepgram API Key"
OPENAI_API_KEY = "Your OpenAI API Key"
ELEVENLABS_API_KEY = "Your ElevenLabs API Key"
VIDEOSDK_AUTH_TOKEN = "VideoSDK Auth token"
Complete Example
For a complete working example with all the code integrated together, check out our GitHub repository: RAG Implementation Example
Implementation
Step 1: Custom Voice Agent with RAG
Create a custom agent class that extends Agent and adds retrieval capabilities:
class VoiceAgent(Agent):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
instructions="""You are a helpful voice assistant that answers questions
based on provided context. Use the retrieved documents to ground your answers.
If no relevant context is found, say so. Be concise and conversational."""
)
# Initialize OpenAI client for embeddings
self.openai_client = AsyncOpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
# Define your knowledge base
self.documents = [
"What is VideoSDK? VideoSDK is a comprehensive video calling and live streaming platform...",
"How do I authenticate with VideoSDK? Use JWT tokens generated with your API key...",
# Add more documents
]
# Set up ChromaDB
self.chroma_client = chromadb.Client() # In-memory
# For persistence: chromadb.PersistentClient(path="./chroma_db")
self.collection = self.chroma_client.create_collection(
name="videosdk_faq_collection"
)
# Generate embeddings and populate database
self._initialize_knowledge_base()
def _initialize_knowledge_base(self):
"""Generate embeddings and store documents."""
embeddings = [self._get_embedding_sync(doc) for doc in self.documents]
self.collection.add(
documents=self.documents,
embeddings=embeddings,
ids=[f"doc_{i}" for i in range(len(self.documents))]
)
Step 2: Embedding Generation
Implement both synchronous (for initialization) and asynchronous (for runtime) embedding methods:
def _get_embedding_sync(self, text: str) -> list[float]:
"""Synchronous embedding for initialization."""
import openai
client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
response = client.embeddings.create(
input=text,
model="text-embedding-ada-002"
)
return response.data[0].embedding
async def get_embedding(self, text: str) -> list[float]:
"""Async embedding for runtime queries."""
response = await self.openai_client.embeddings.create(
input=text,
model="text-embedding-ada-002"
)
return response.data[0].embedding
Step 3: Retrieval Method
Add semantic search capability:
async def retrieve(self, query: str, k: int = 2) -> list[str]:
"""Retrieve top-k most relevant documents from vector database."""
# Generate query embedding
query_embedding = await self.get_embedding(query)
# Query ChromaDB
results = self.collection.query(
query_embeddings=[query_embedding],
n_results=k
)
# Return matching documents
return results["documents"][0] if results["documents"] else []
Step 4: Agent Lifecycle Hooks
Define agent behavior on entry and exit:
async def on_enter(self) -> None:
"""Called when agent session starts."""
await self.session.say("Hello! I'm your VideoSDK assistant. How can I help you today?")
async def on_exit(self) -> None:
"""Called when agent session ends."""
await self.session.say("Thank you for using VideoSDK. Goodbye!")
Step 5: Custom Conversation Flow
Override the conversation flow to inject retrieved context:
class RAGConversationFlow(ConversationFlow):
async def run(self, transcript: str) -> AsyncIterator[str]:
"""
Process user input with RAG pipeline.
Args:
transcript: User's speech transcribed to text
Yields:
Generated response chunks
"""
# Step 1: Retrieve relevant documents
context_docs = await self.agent.retrieve(transcript)
# Step 2: Format context
if context_docs:
context_str = "\n\n".join([f"Document {i+1}: {doc}"
for i, doc in enumerate(context_docs)])
else:
context_str = "No relevant context found."
# Step 3: Inject context into conversation
self.agent.chat_context.add_message(
role="system",
content=f"Retrieved Context:\n{context_str}\n\nUse this context to answer the user's question."
)
# Step 4: Generate response with LLM
async for response_chunk in self.process_with_llm():
yield response_chunk
Step 6: Session and Pipeline Setup
Configure the agent session and start the job:
async def entrypoint(ctx: JobContext):
agent = VoiceAgent()
conversation_flow = RAGConversationFlow(
agent=agent,
)
session = AgentSession(
agent=agent,
pipeline=CascadingPipeline(
stt=DeepgramSTT(),
llm=OpenAILLM(),
tts=ElevenLabsTTS(),
vad=SileroVAD(),
turn_detector=TurnDetector()
),
conversation_flow=conversation_flow,
)
# Register cleanup
ctx.add_shutdown_callback(lambda: session.close())
# Start agent
try:
await ctx.connect()
print("Waiting for participant...")
await ctx.room.wait_for_participant()
print("Participant joined - starting session")
await session.start()
await asyncio.Event().wait()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nShutting down gracefully...")
finally:
await session.close()
await ctx.shutdown()
def make_context() -> JobContext:
room_options = RoomOptions(name="RAG Voice Assistant", playground=True)
return JobContext(room_options=room_options)
if __name__ == "__main__":
job = WorkerJob(entrypoint=entrypoint, jobctx=make_context)
job.start()
Advanced Features
Dynamic Document Updates
Add documents at runtime:
async def add_document(self, document: str, metadata: dict = None):
"""Add a new document to the knowledge base."""
doc_id = f"doc_{len(self.documents)}"
embedding = await self.get_embedding(document)
self.collection.add(
documents=[document],
embeddings=[embedding],
ids=[doc_id],
metadatas=[metadata] if metadata else None
)
self.documents.append(document)
Document Chunking
Split large documents for better retrieval:
def chunk_document(self, document: str, chunk_size: int = 500, overlap: int = 50) -> list[str]:
"""Split document into overlapping chunks."""
words = document.split()
chunks = []
for i in range(0, len(words), chunk_size - overlap):
chunk = " ".join(words[i:i + chunk_size])
chunks.append(chunk)
return chunks
# Use when adding documents
for doc in large_documents:
chunks = self.chunk_document(doc)
for chunk in chunks:
self.documents.append(chunk)
Best Practices
- Document Quality: Use clear, well-structured documents with specific information
- Chunk Size: Keep chunks between 300-800 words for optimal retrieval
- Retrieval Count: Start with k=2-3, adjust based on response quality and latency
- Context Window: Ensure retrieved context fits within LLM token limits
- Persistent Storage: Use PersistentClient in production to save embeddings
- Error Handling: Always handle retrieval failures gracefully
- Testing: Test with diverse queries to ensure good coverage
Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Slow responses | Reduce retrieval count (k), use faster embedding model, or cache embeddings |
| Irrelevant results | Improve document quality, adjust chunking strategy, or use metadata filtering |
| Out of memory | Use PersistentClient instead of in-memory Client |
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

