Quick Start for Http Live Streaming(HLS) in iOS
VideoSDK empowers you to seamlessly integrate the Http Live Streaming(HLS) feature into your iOS application within minutes.
In this quickstart, you'll explore this feature of VideoSDK. Follow the step-by-step guide to integrate it within your application.
For low-latency interactive live streaming (under 100ms), follow this documentation.
Prerequisites
- iOS 13.0+
- Xcode 15.0+
- Swift 5.0+
One should have a VideoSDK account to generate token. Visit VideoSDK dashboard to generate token
App Architecture
The application consists of two primary interfaces:
Start Meeting View
- Allows users to create a new meeting or join an existing one by selecting their mode (Host or Viewer/Audience)
Meeting View
- Provides Http Live Stream controls and adapts the UI dynamically based on the user's mode (Host or Viewer/Audience).
Getting Started With the Code!
Follow the steps to create the environment necessary to add video calls into your app. Also you can find the code sample for quickstart here.
Important Changes iOS SDK in Version v2.2.0
- The following modes have been deprecated:
CONFERENCEhas been replaced bySEND_AND_RECVVIEWERhas been replaced bySIGNALLING_ONLY
Please update your implementation to use the new modes.
⚠️ Compatibility Notice:
To ensure a seamless meeting experience, all participants must use the same SDK version.
Do not mix version v2.2.0 + with older versions, as it may cause significant conflicts.
Step 1: Create New iOS Application
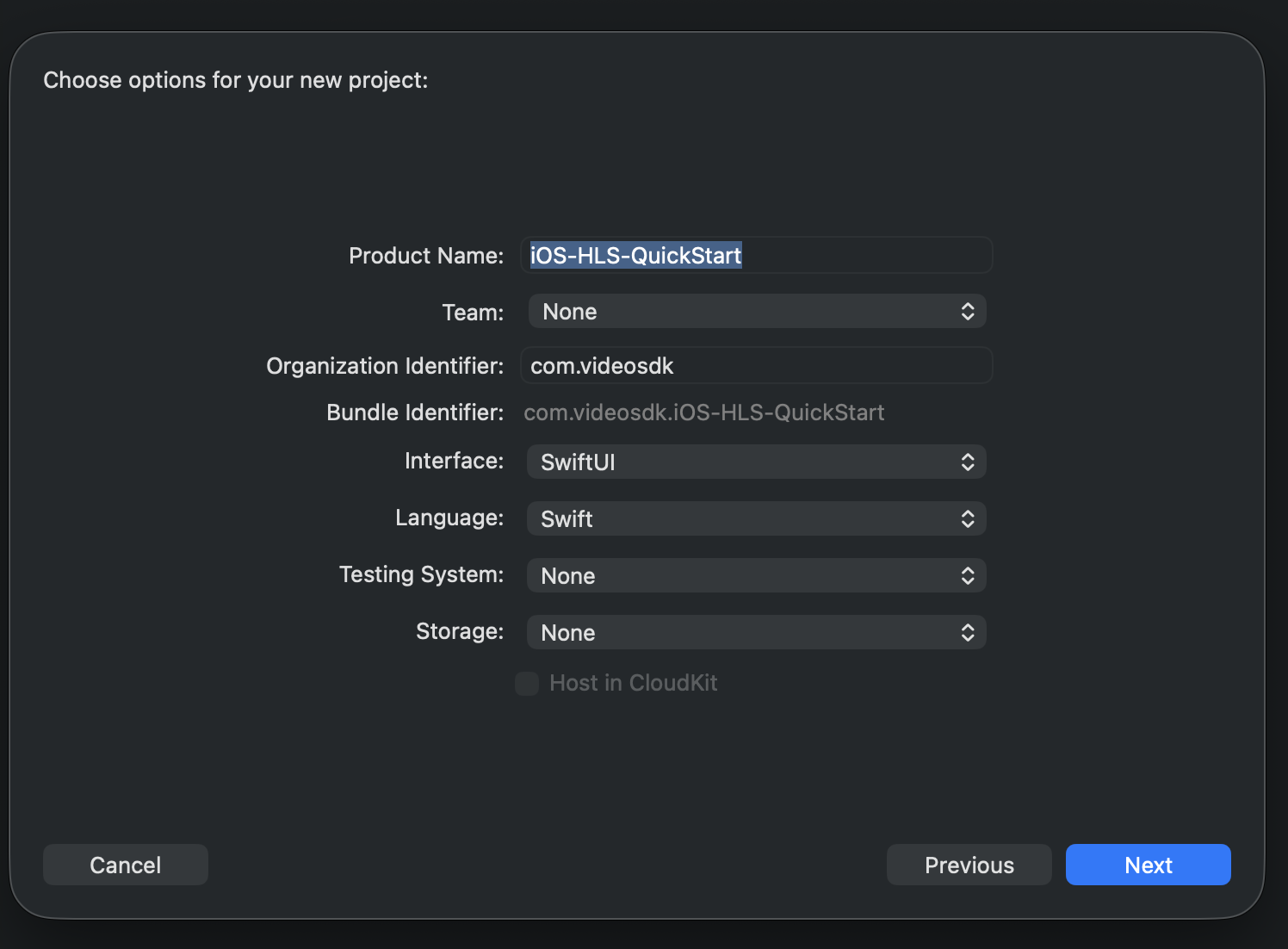
Step 1: Create a new application by selecting Create a new Xcode project
Step 2: Add Product Name and Save the project.
Step 2: VideoSDK Installation
There are two ways to install VideoSDK: Using Swift Package Manager (SPM) or Using CocoaPods.
1. Install Using Swift Package Manager (SPM)
To install VideoSDK via Swift Package Manager, follow these steps:
- Open your Xcode project and go to File > Add Packages.
- Enter the repository URL:
https://github.com/videosdk-live/videosdk-rtc-ios-spm
- Choose the version rule (e.g., "Up to Next Major") and add the package to your target.
- Import the library in Swift files:
import VideoSDKRTC
For more details, refer to the official guide on SPM installation.
2. Install Using CocoaPods
To install VideoSDK using CocoaPods, follow these steps:
- Initialize CocoaPods: Run the following command in your project directory:
pod init
- Update the Podfile: Open the Podfile and add the VideoSDK dependency:
pod 'VideoSDKRTC', :git => 'https://github.com/videosdk-live/videosdk-rtc-ios-sdk.git'
- Install the Pod: Run the following command to install the pod:
pod install
For more details, refer to the official guide on CocoaPods installation.
then declare the permissions in Info.plist :
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Camera permission description</string>
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Microphone permission description</string>
Step 3: Project Structure
quick_start_ios_hls
├── quick_start_ios_hls.swift // Default
├── Screens
├── StartMeetingView.swift
└── Meeting
├── Controller
└── MeetingViewController.swift
└── MeetingView.swift
├── Views
├── HLSPlayer.swift
└── ParticipantViewItem.swift
├── Model
└── RoomStruct.swift
└── Info.plist // Default
Pods
└── Podfile
Step 4: Create Start Meeting View
The StartMeetingView acts as the entry point for users to initiate or participate in Http Live Streams with the following functionalities:
-
Create Meeting as Host: Start a new Http Live Stream in
SEND_AND_RECVmode, providing full host privileges. -
Join as Host: Enter an existing Http Live Stream with
SEND_AND_RECVmode, granting full host controls. -
Join as Viewer: Join an existing Http Live Stream with
SIGNALLING_ONLYmode, without receiving & producing audio & video.
- Swift
import SwiftUI
// MARK: - Meeting Role Enum
enum UserRole: String { case host = "Host", case viewer = "Viewer" }
struct StartMeetingView: View {
//MARK: - Properties
@State private var meetingId: String = "<MeetingID goes here>"
@State private var navigateToMeeting = false
@State private var selectedRole: UserRole = .host
@State private var animateButtons = false
@State private var isLoading = false
var body: some View {
NavigationStack {
ZStack {
// Background
LinearGradient(
colors: [Color.black, Color.black.opacity(0.9)],
startPoint: .top,
endPoint: .bottom
)
.ignoresSafeArea()
VStack(spacing: 30) {
Image("logo")
.resizable()
.renderingMode(.original)
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(width: 175, height: 175)
.cornerRadius(25)
.shadow(color: .white.opacity(0.5), radius: 20)
Spacer()
// Create Meeting Button
animatedButton(title: "Create Meeting", bgColor: .blue) {
if (!isLoading) {
Task {
await createMeeting()
}
}
}
// Meeting ID TextField
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 8) {
Text("Enter Meeting ID")
.font(.headline)
.foregroundColor(.white.opacity(0.8))
ZStack {
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 14)
.fill(Color.white)
.frame(height: 55)
TextField("", text: $meetingId)
.foregroundColor(.black)
.padding(.horizontal)
.textInputAutocapitalization(.never)
}
}
.padding(.horizontal)
// Host + Viewer Buttons
HStack(spacing: 5) {
animatedButton(title: "Join as Host", bgColor: .green) {
selectedRole = .host
navigateToMeeting = true
}
animatedButton(title: "Join as Viewer", bgColor: .orange) {
selectedRole = .viewer
navigateToMeeting = true
}
}
Spacer()
}
.padding()
}
.navigationDestination(isPresented: $navigateToMeeting) {
MeetingView(meetingId: meetingId, role: selectedRole)
}
}
}
// MARK: - API: Create Meeting
func createMeeting() async {
guard let url = URL(string: "https://api.videosdk.live/v2/rooms") else { return }
isLoading = true
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.httpMethod = "POST"
request.addValue(AUTH_TOKEN, forHTTPHeaderField: "Authorization")
do {
let (data, _) = try await URLSession.shared.data(for: request)
let decoded = try JSONDecoder().decode(RoomsStruct.self, from: data)
await MainActor.run {
if let roomId = decoded.roomID {
self.meetingId = roomId
self.selectedRole = .host
self.navigateToMeeting = true
}
}
} catch {
print("Meeting creation failed:", error)
}
isLoading = false
}
// MARK: - Reusable Animated Button
@ViewBuilder
func animatedButton(title: String, bgColor: Color, action: @escaping () -> Void) -> some View {
Button(action: {
withAnimation(.spring(response: 0.25, dampingFraction: 0.5)) {
action()
}
}) {
Text(title)
.font(.headline)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.padding(.horizontal, 5)
.frame(height: 55)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
.background(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 16)
.fill(bgColor.opacity(0.85))
.shadow(color: bgColor.opacity(0.6), radius: 10, x: 0, y: 4)
)
}
.scaleEffect(animateButtons ? 1 : 0.85)
.animation(.spring(response: 0.5, dampingFraction: 0.6), value: animateButtons)
.padding(.horizontal, 5)
}
}
Output
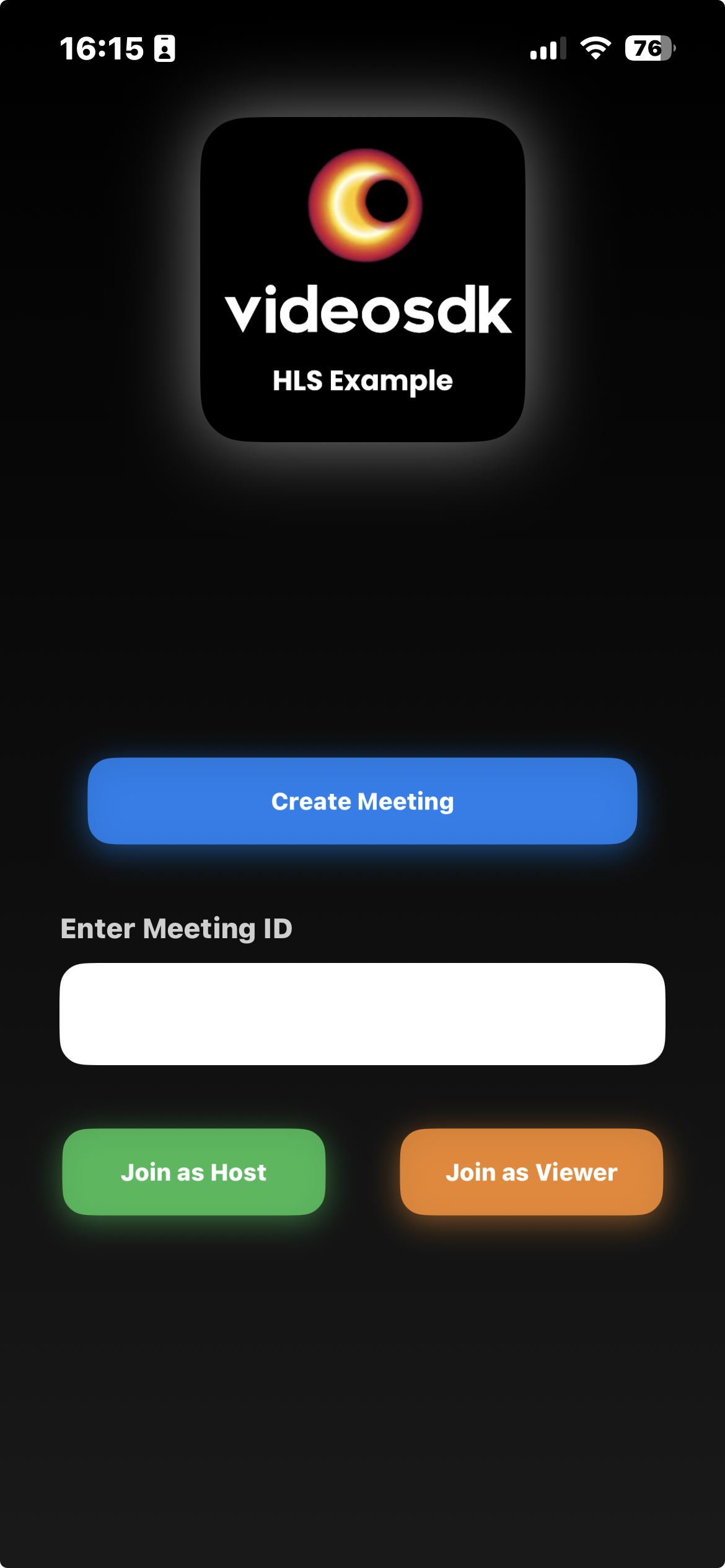
Also add the StartMeetingView in main app as shown below
- Swift
import SwiftUI
@main
struct quick_start_ios_hls: App {
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
StartMeetingView()
}
}
}
Before proceeding, let's understand the two modes of a HTTP Live Stream:
1. SEND_AND_RECV (For Host or Co-host):
- Designed primarily for the Host or Co-host.
- Allows sending and receiving media.
- Hosts can broadcast their audio/video and interact directly with the audience.
2. SIGNALLING_ONLY (For Viewer/Audience):
- Tailored for the Viewer/Audience.
- Doesn't enabled receiving media shared by the Host also.
- Audience members can not view or listen, also cannot share their own media.
Step 5: Initialize and Join the Http Live Stream
In this step, Inside MeetingViewController we will setup initializeMeeting and related functions for it. You will require Auth token, you can generate it using either using videosdk-server-api-example or generate it from the Video SDK Dashboard for developer.
MeetingViewController will implement various event listeners such as MeetingEventListener, ParticipantEventListener.
- Swift
import Foundation
import SwiftUI
import Combine
import VideoSDKRTC
internal import Mediasoup
// MARK: - MeetingViewController
class MeetingViewController: ObservableObject {
@Published var participants: [Participant] = []
@Published var hlsState: HLSState = .HLS_STOPPED
@Published var isMicOn: Bool = true
@Published var isWebcamOn: Bool = true
@Published var meeting: Meeting? = nil
@Published var participantVideoTracks: [String: RTCVideoTrack] = [:]
@Published var participantMicStatus: [String: Bool] = [:]
@Published var playbackURL: String? = nil
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
let meetingId: String
let role: UserRole
init(meetingId: String, role: UserRole) {
self.meetingId = meetingId
self.role = role
// Auto-start meeting logic when created
initializeMeeting()
}
// MARK: - Meeting Initialization
func initializeMeeting() {
VideoSDK.config(token: AUTH_TOKEN)
let videoMediaTrack = try? VideoSDK.createCameraVideoTrack(
encoderConfig: .h720p_w1280p,
facingMode: .front,
multiStream: true
)
meeting = VideoSDK.initMeeting(
meetingId: meetingId,
participantName: "John doe",
micEnabled: self.isMicOn,
webcamEnabled: self.isWebcamOn,
customCameraVideoStream: videoMediaTrack,
multiStream: true,
mode: self.role == .viewer ? .SIGNALLING_ONLY : .SEND_AND_RECV
)
// Add event listeners and join the meeting
meeting?.addEventListener(self)
meeting?.join()
}
// MARK: - HLS Handling
func startHLS() {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.startHLS()
}
}
func stopHLS() {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.stopHLS()
}
}
// MARK: - Media Toggles
func toggleMic() {
if (isMicOn) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.muteMic()
}
} else {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.unmuteMic()
}
}
isMicOn.toggle()
}
func toggleWebcam() {
if (isWebcamOn) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.disableWebcam()
}
} else {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.meeting?.enableWebcam()
}
}
isWebcamOn.toggle()
}
// MARK: - Leave Meeting
func leaveMeeting() {
if (role == .host) {
if (self.hlsState == .HLS_STARTED || self.hlsState == .HLS_PLAYABLE || self.hlsState == .HLS_STARTING) {
self.meeting?.stopHLS()
}
}
self.meeting?.leave()
}
}
extension MeetingViewController: MeetingEventListener {
func onMeetingJoined() {
guard let localParticipant = self.meeting?.localParticipant else { return }
let isExist = participants.first { $0.id == localParticipant.id } != nil
if (!isExist && (localParticipant.mode != .SIGNALLING_ONLY && localParticipant.mode != .VIEWER)) {
participants.append(localParticipant)
}
// add event listener
localParticipant.addEventListener(self)
}
//...
}
extension MeetingViewController: ParticipantEventListener {
func onStreamEnabled(_ stream: MediaStream, forParticipant participant: Participant) {
if let track = stream.track as? RTCVideoTrack {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
if case .state(let mediaKind) = stream.kind, mediaKind == .video {
self.participantVideoTracks[participant.id] = track
}
}
}
if case .state(let mediaKind) = stream.kind, mediaKind == .audio {
self.participantMicStatus[participant.id] = true // Mic enabled
}
}
func onStreamDisabled(_ stream: MediaStream, forParticipant participant: Participant) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
if case .state(let mediaKind) = stream.kind, mediaKind == .video {
self.participantVideoTracks.removeValue(forKey: participant.id)
}
}
if case .state(let mediaKind) = stream.kind, mediaKind == .audio {
// Update microphone state for this participant
self.participantMicStatus[participant.id] = false // Mic disabled
}
}
}
Step 6: Create ParticipantViewItem View
The ParticipantViewItem file manages the participant view for particular participant which is showed in the participants which is host in the meeting.
- Swift
import VideoSDKRTC
import SwiftUI
internal import Mediasoup
struct ParticipantContainerView: View {
let participant: Participant
@ObservedObject var controller: MeetingViewController
var body: some View {
ZStack {
participantView(participant: participant, controller: controller)
VStack {
Spacer()
HStack {
// Participant name
Text(participant.displayName)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.padding(.horizontal, 8)
.padding(.vertical, 4)
.background(Color.black.opacity(0.5))
.cornerRadius(4)
// Mic status indicator
Image(systemName: controller.participantMicStatus[participant.id] ?? false ? "mic.fill" : "mic.slash.fill")
.foregroundColor(controller.participantMicStatus[participant.id] ?? false ? .green : .red)
.padding(4)
.background(Color.black.opacity(0.5))
.clipShape(Circle())
Spacer()
}
.padding(8)
}
}
.background(Color.black.opacity(0.9)) // Background color
.cornerRadius(10) // Rounded corners
.shadow(color: Color.gray.opacity(0.7), radius: 10, x: 0, y: 5) // Shadow effect
.overlay(
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10) // Rounded border
.stroke(Color.gray.opacity(0.9), lineWidth: 1)
)
}
private func participantView(participant: Participant, controller: MeetingViewController) -> some View {
ZStack {
ParticipantView(participant: participant, controller: controller)
}
}
}
/// VideoView for participant's video
class VideoView: UIView {
var videoView: RTCMTLVideoView = {
let view = RTCMTLVideoView()
view.videoContentMode = .scaleAspectFill
view.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
view.clipsToBounds = true
view.transform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: 1, y: 1)
return view
}()
init(track: RTCVideoTrack?, frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
backgroundColor = .clear
// Set videoView frame to match parent view
videoView.frame = bounds
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.addSubview(self.videoView)
self.bringSubviewToFront(self.videoView)
track?.add(self.videoView)
}
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
// Update videoView frame when parent view size changes
videoView.frame = bounds
}
}
/// ParticipantView for showing and hiding VideoView
struct ParticipantView: View {
let participant: Participant
@ObservedObject var controller: MeetingViewController
var body: some View {
ZStack {
if let track = controller.participantVideoTracks[participant.id] {
VideoStreamView(track: track)
} else {
Color.white.opacity(1.0)
Text("No media")
.font(.largeTitle)
.foregroundStyle(.black)
}
}
}
}
struct VideoStreamView: UIViewRepresentable {
let track: RTCVideoTrack
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> VideoView {
let view = VideoView(track: track, frame: .zero)
return view
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: VideoView, context: Context) {
track.add(uiView.videoView)
uiView.videoView.videoContentMode = .scaleAspectFill
}
}
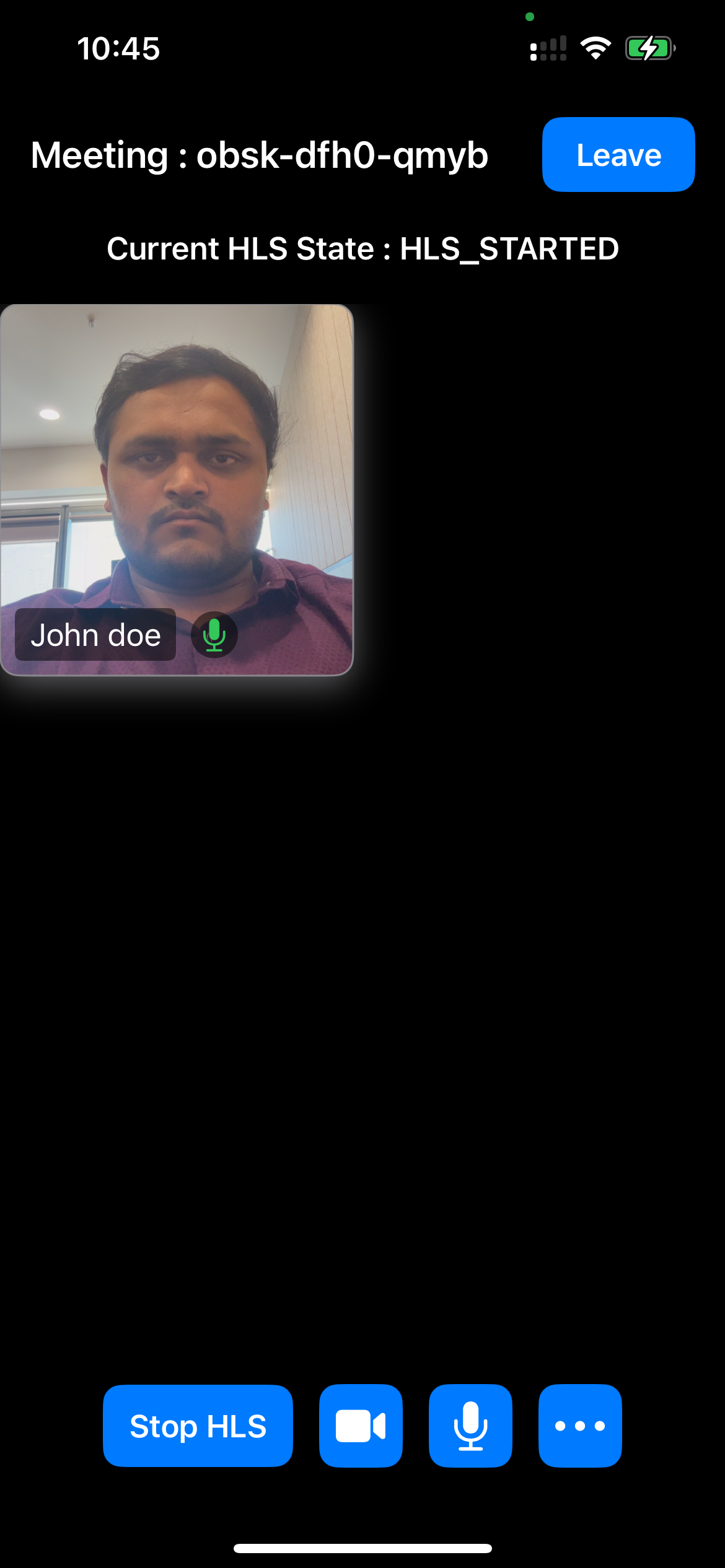
Output

Step 7: Implementing Media Toggles and Start/Stop HLS
Host Controls: Include buttons to toggle the microphone, webcam and HLS, allowing users to mute/unmute their microphone and enable/disable their camera and start/stop the HLS entirely.
Header UI: Includes button for leave the meeting and meetingId also displayed in the Header UI.
- Swift
import SwiftUI
import VideoSDKRTC
struct MeetingView: View {
@StateObject private var controller: MeetingViewController
@Environment(\.dismiss) var dismiss
init(meetingId: String, role: UserRole) {
_controller = StateObject(
wrappedValue: MeetingViewController(meetingId: meetingId, role: role)
)
}
// Grid layout
private let columns = [
GridItem(.flexible(), spacing: 10),
GridItem(.flexible(), spacing: 10),
]
var body: some View {
ZStack {
Color.black.ignoresSafeArea()
VStack(spacing: 20) {
// HEADER
header
if controller.role == .host {
// HLS State
Text("Current HLS State : \(controller.hlsState.rawValue)")
.foregroundColor(.white)
.font(.headline)
// Participants Grid
ScrollView {
LazyVGrid(columns: columns) {
ForEach(controller.participants, id: \.id) { participant in
ParticipantContainerView(
participant: participant,
controller: controller
)
.frame(height: 200, alignment: .center)
}
}
}
Spacer()
} else {
if ((controller.hlsState == .HLS_STARTED || controller.hlsState == .HLS_PLAYABLE) && controller.playbackURL != nil) {
HLSVideoPlayer(
url: URL(string: controller.playbackURL ?? "")!,
width: .infinity,
height: .infinity
)
.cornerRadius(12)
.padding()
Spacer()
} else {
Spacer()
Text("Waiting for host\nto start the live streaming")
.font(.title)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.bold(true)
.multilineTextAlignment(.center)
Spacer()
}
}
// Host Controls
if controller.role == .host {
hostControls
}
}
}
.navigationBarBackButtonHidden(true)
.navigationBarHidden(true)
}
// MARK: Header UI
private var header: some View {
HStack {
Text("Meeting : \(controller.meetingId)")
.foregroundColor(.white)
.font(.title3.bold())
Spacer()
Button {
controller.leaveMeeting()
dismiss()
} label: {
Text("Leave")
.font(.headline)
.padding(.horizontal, 18)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
.padding(.horizontal)
.padding(.top)
}
// MARK: Host bottom controls
private var hostControls: some View {
HStack(spacing: 14) {
if (controller.hlsState == .HLS_STARTING || controller.hlsState == .HLS_STARTED || controller.hlsState == .HLS_PLAYABLE) {
controlButton(title: "Stop HLS") {
controller.stopHLS()
}
} else {
controlButton(title: "Start HLS") {
controller.startHLS()
}
}
controlButton(title: "Toggle Webcam") {
controller.toggleWebcam()
}
controlButton(title: "Toggle Mic") {
controller.toggleMic()
}
}
.padding(.bottom, 20)
}
// MARK: Reusable UI Elements
func controlButton(title: String, action: @escaping () -> Void) -> some View {
Button(action: action) {
Text(title)
.font(.headline)
.padding(.horizontal, 14)
.padding(.vertical, 12)
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundColor(.white)
.cornerRadius(10)
}
}
}
Output
Step 8: Extending Meeting Event Listeners
In this step, we extend the MeetingEventListener implementation in MeetingViewController by adding additional event listeners for enhanced meeting functionality.
These include onParticipantJoined and onParticipantLeft to handle participant updates, onMeetingStateChanged to manage meeting state transitions, and onHlsStateChanged to track HLS state, allowing us to utilize them as needed.
- Swift
class MeetingViewController: ObservableObject {
//...
extension MeetingViewController: MeetingEventListener {
//...
func onParticipantJoined(_ participant: Participant) {
let isExist = participants.first { $0.id == participant.id } != nil
if (!isExist && (participant.mode != .SIGNALLING_ONLY && participant.mode != .VIEWER)) {
participants.append(participant)
}
// add listener
participant.addEventListener(self)
}
func onParticipantLeft(_ participant: Participant) {
participants = participants.filter({ $0.id != participant.id })
}
func onMeetingStateChanged(meetingState: MeetingState) {
switch meetingState {
case .DISCONNECTED:
participants.removeAll()
default:
print("meeting state: \(meetingState.rawValue)")
}
}
func onHlsStateChanged(state: HLSState, hlsUrl: HLSUrl?) {
hlsState = state
switch (state) {
case .HLS_PLAYABLE:
playbackURL = hlsUrl?.playbackHlsUrl ?? ""
default:
print("HLS State: \(state.rawValue)")
}
}
}
//...
}
Output
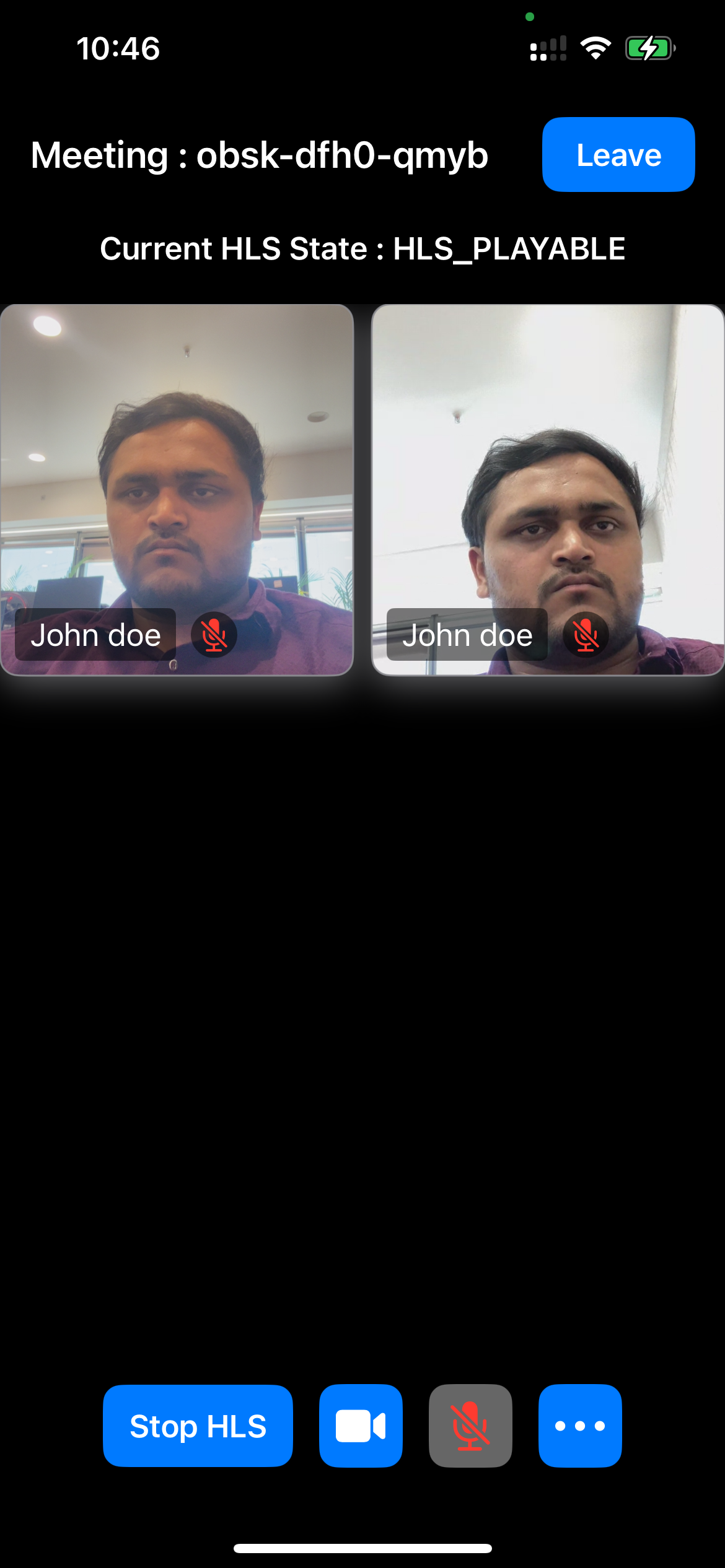
Final Output
We are done with implementation of HLS Live Streaming in iOS Appplication using Video SDK. To explore more features go through Basic and Advanced features.
Stuck anywhere? Check out this example code on GitHub
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

