Quick Start for Conference in React Native
VideoSDK enables the opportunity to integrate video & audio calling to Web, Android, iOS applications. It provides Programmable SDKs and REST APIs to build scalable video conferencing applications.
This guide will get you running with the VideoSDK video & audio calling in minutes.
Prerequisites
- Node.js v12+
- NPM v6+ (comes installed with newer Node versions)
- Android Studio or Xcode installed
App Architecture
This App will contain two screen :
-
Join Screen: This screen allows user to either create meeting or join predefined meeting. -
Meeting Screen: This screen basically contain participant list and some meeting controls such as Enable / Disable Mic & Camera and Leave meeting.
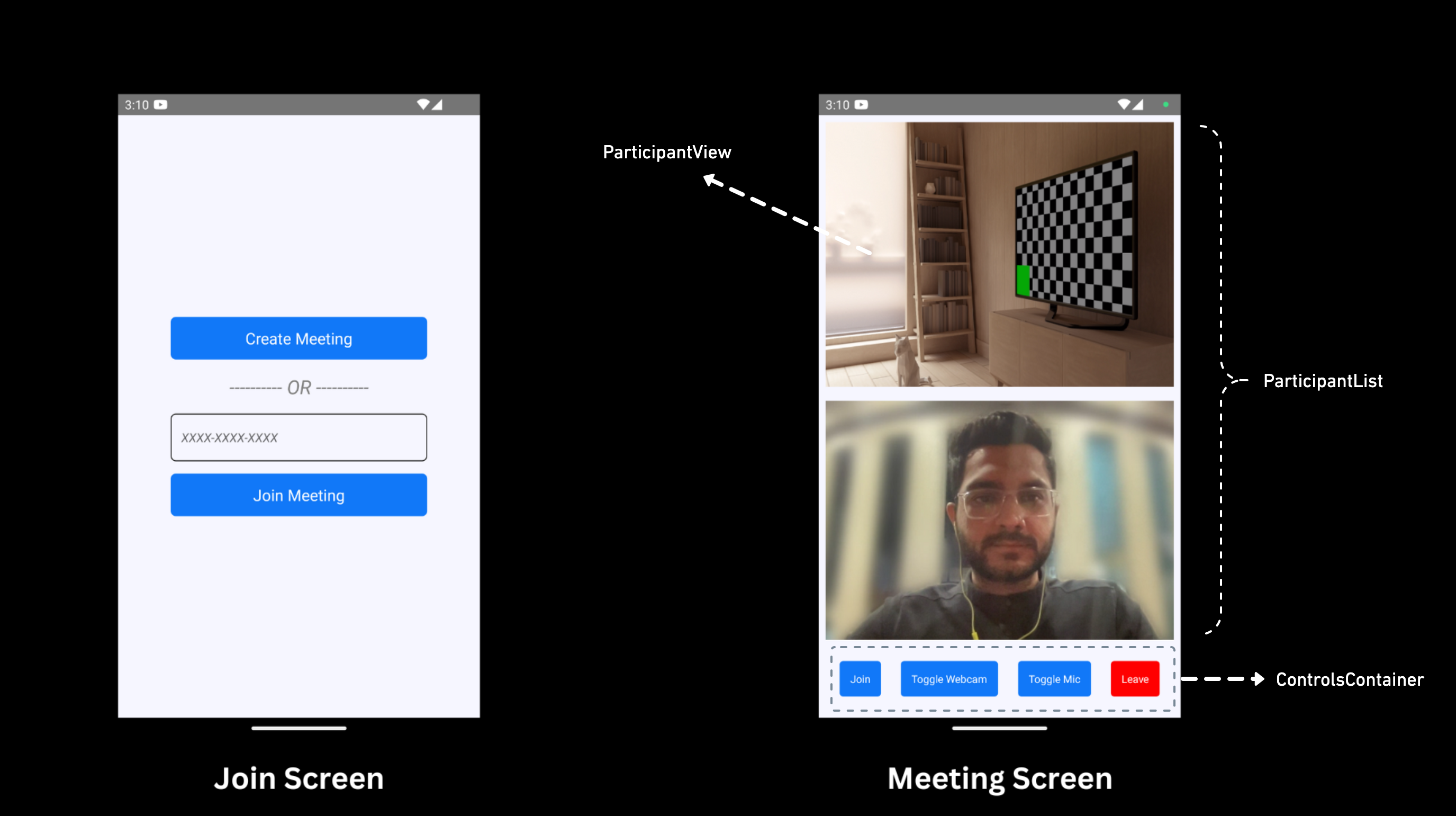
Getting Started with the Code!
Create App
Create new react-native app by applying below commands.
npx react-native init AppName
For react-native setup, you can follow Official Docs.
VideoSDK Installation
Install the VideoSDK by following the below command. Do make sure you should be in your project directory before you run this command.
- NPM
- Yarn
npm install "@videosdk.live/react-native-sdk" "@videosdk.live/react-native-incallmanager"
yarn add "@videosdk.live/react-native-sdk" "@videosdk.live/react-native-incallmanager"
Project Structure
root
├── node_modules
├── android
├── ios
├── App.js
├── api.js
├── index.js
Project Configuration
Android Setup
- Add required permission in AndroidManifest.xml file.
<manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.cool.app"
>
<!-- Give all the required permissions to app -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<!-- Needed to communicate with already-paired Bluetooth devices. (Legacy up to Android 11) -->
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH"
android:maxSdkVersion="30" />
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"
android:maxSdkVersion="30" />
<!-- Needed to communicate with already-paired Bluetooth devices. (Android 12 upwards)-->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK" />
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="live.videosdk.rnfgservice.notification_channel_name"
android:value="Meeting Notification"
/>
<meta-data
android:name="live.videosdk.rnfgservice.notification_channel_description"
android:value="Whenever meeting started notification will appear."
/>
<meta-data
android:name="live.videosdk.rnfgservice.notification_color"
android:resource="@color/red"
/>
<service android:name="live.videosdk.rnfgservice.ForegroundService" android:foregroundServiceType="mediaProjection"></service>
<service android:name="live.videosdk.rnfgservice.ForegroundServiceTask"></service>
</application>
</manifest>
- Update colors.xml for internal dependencies
<resources>
<item name="red" type="color">
#FC0303
</item>
<integer-array name="androidcolors">
<item>@color/red</item>
</integer-array>
</resources>
- Linking VideoSDK Dependencies.
dependencies {
implementation project(':rnwebrtc')
implementation project(':rnfgservice')
}
include ':rnwebrtc'
project(':rnwebrtc').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/@videosdk.live/react-native-webrtc/android')
include ':rnfgservice'
project(':rnfgservice').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/@videosdk.live/react-native-foreground-service/android')
import live.videosdk.rnwebrtc.WebRTCModulePackage;
import live.videosdk.rnfgservice.ForegroundServicePackage;
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
private static List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
@SuppressWarnings("UnnecessaryLocalVariable")
List<ReactPackage> packages = new PackageList(this).getPackages();
// Packages that cannot be autolinked yet can be added manually here, for example:
packages.add(new ForegroundServicePackage());
packages.add(new WebRTCModulePackage());
return packages;
}
}
/* This one fixes a weird WebRTC runtime problem on some devices. */
android.enableDexingArtifactTransform.desugaring=false
- Add below line in the proguard-rules.pro (optional: if you are using Proguard)
-keep class org.webrtc.** { *; }
- In the
build.gradlefile, update the minimum OS/SDK version to23.
buildscript {
ext {
minSdkVersion = 23
}
}
iOS Setup
- IMPORTANT: Make sure you are using CocoaPods 1.10 or higher.
To update CocoaPods you simply install the gem again
$ sudo gem install cocoapods
- Manual linking (if react-native-incall-manager is not linked automatically)
- Select
Your_Xcode_Project/TARGETS/BuildSettings, in Header Search Paths, add"$(SRCROOT)/../node_modules/@videosdk.live/react-native-incall-manager/ios/RNInCallManager"
- Change path of
react-native-webrtc
pod ‘react-native-webrtc’, :path => ‘../node_modules/@videosdk.live/react-native-webrtc’
- Change your platform version
You have change platform field of podfile to 12.0 or above it, as react-native-webrtc doesn’t support iOS < 12 platform :ios, ‘12.0’
- Install pods
After updating the version, you have to install pods.
Pod install
- Declare permissions in Info.plist :
Add following lines to info.plist (project folder/ios/projectname/info.plist):
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Camera permission description</string>
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Microphone permission description</string>
Register Service
Register VideoSDK services in root index.js file for initialization service.
import { AppRegistry } from "react-native";
import App from "./App";
import { name as appName } from "./app.json";
import { register } from "@videosdk.live/react-native-sdk";
register();
AppRegistry.registerComponent(appName, () => App);
Step 1 : Get started with api.js
Before jumping to anything else, we have write API to generate unique meetingId. You will require auth token, you can generate it using either by using videosdk-rtc-api-server-examples or generate it from the Video SDK Dashboard for developer.
export const token = "<Generated-from-dashbaord>";
// API call to create meeting
export const createMeeting = async ({ token }) => {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.videosdk.live/v2/rooms`, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
authorization: `${token}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({}),
});
const { roomId } = await res.json();
return roomId;
};
Step 2: Wireframe App.js with all the components
To build up wireframe of App.js, we are going to use Video SDK Hooks and Context Providers. Video SDK provideos MeetingProvider, MeetingConsumer, useMeeting and useParticipant hooks. Let's understand each of them.
First we will explore Context Provider and Consumer. Context is primarily used when some data needs to be accessible by many components at different nesting levels.
- MeetingProvider: It is Context Provider. It accepts value
configandtokenas props. The Provider component accepts a value prop to be passed to consuming components that are descendants of this Provider. One Provider can be connected to many consumers. Providers can be nested to override values deeper within the tree. - MeetingConsumer: It is Context Consumer. All consumers that are descendants of a Provider will re-render whenever the Provider’s value prop changes.
- useMeeting: It is meeting react hook API for meeting. It includes all the information related to meeting such as join, leave, enable/disable mic or webcam etc.
- useParticipant: It is participant hook API. useParticipant hook is responsible to handle all the events and props related to one particular participant such as name, webcamStream, micStream etc.
Meeting Context helps to listen on all the changes when participant joines meeting or changes mic or camera etc.
Let's get started with change couple of lines of code in App.js
import React, { useState } from "react";
import {
SafeAreaView,
TouchableOpacity,
Text,
TextInput,
View,
FlatList,
} from "react-native";
import {
MeetingProvider,
useMeeting,
useParticipant,
MediaStream,
RTCView,
} from "@videosdk.live/react-native-sdk";
import { createMeeting, token } from "./api";
function JoinScreen(props) {
return null;
}
function ControlsContainer() {
return null;
}
function MeetingView() {
return null;
}
export default function App() {
const [meetingId, setMeetingId] = useState(null);
const getMeetingId = async (id) => {
const meetingId = id == null ? await createMeeting({ token }) : id;
setMeetingId(meetingId);
};
return meetingId ? (
<SafeAreaView style={{ flex: 1, backgroundColor: "#F6F6FF" }}>
<MeetingProvider
config={{
meetingId,
micEnabled: false,
webcamEnabled: true,
name: "Test User",
}}
token={token}
>
<MeetingView />
</MeetingProvider>
</SafeAreaView>
) : (
<JoinScreen getMeetingId={getMeetingId} />
);
}
Step 3 : Implement Join Screen
Join screen will work as medium to either schedule new meeting or to join existing meeting.
function JoinScreen(props) {
const [meetingVal, setMeetingVal] = useState("");
return (
<SafeAreaView
style={{
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: "#F6F6FF",
justifyContent: "center",
paddingHorizontal: 6 * 10,
}}
>
<TouchableOpacity
onPress={() => {
props.getMeetingId();
}}
style={{ backgroundColor: "#1178F8", padding: 12, borderRadius: 6 }}
>
<Text style={{ color: "white", alignSelf: "center", fontSize: 18 }}>
Create Meeting
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<Text
style={{
alignSelf: "center",
fontSize: 22,
marginVertical: 16,
fontStyle: "italic",
color: "grey",
}}
>
---------- OR ----------
</Text>
<TextInput
value={meetingVal}
onChangeText={setMeetingVal}
placeholder={"XXXX-XXXX-XXXX"}
style={{
padding: 12,
borderWidth: 1,
borderRadius: 6,
fontStyle: "italic",
}}
/>
<TouchableOpacity
style={{
backgroundColor: "#1178F8",
padding: 12,
marginTop: 14,
borderRadius: 6,
}}
onPress={() => {
props.getMeetingId(meetingVal);
}}
>
<Text style={{ color: "white", alignSelf: "center", fontSize: 18 }}>
Join Meeting
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
Output

Step 4 : Implement Controls
Next step is to create a ControlsContainer component that manage features such as Join or Leave Meeting and Enable or Disable Webcam/Mic.
In this steps we will use useMeeting hook to get all required method such as join(), leave(), toggleWebcam and toggleMic.
const Button = ({ onPress, buttonText, backgroundColor }) => {
return (
<TouchableOpacity
onPress={onPress}
style={{
backgroundColor: backgroundColor,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
padding: 12,
borderRadius: 4,
}}
>
<Text style={{ color: "white", fontSize: 12 }}>{buttonText}</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
);
};
function ControlsContainer({ join, leave, toggleWebcam, toggleMic }) {
return (
<View
style={{
padding: 24,
flexDirection: "row",
justifyContent: "space-between",
}}
>
<Button
onPress={() => {
join();
}}
buttonText={"Join"}
backgroundColor={"#1178F8"}
/>
<Button
onPress={() => {
toggleWebcam();
}}
buttonText={"Toggle Webcam"}
backgroundColor={"#1178F8"}
/>
<Button
onPress={() => {
toggleMic();
}}
buttonText={"Toggle Mic"}
backgroundColor={"#1178F8"}
/>
<Button
onPress={() => {
leave();
}}
buttonText={"Leave"}
backgroundColor={"#FF0000"}
/>
</View>
);
}
function ParticipantList() {
return null;
}
function MeetingView() {
const { join, leave, toggleWebcam, toggleMic, meetingId } = useMeeting({});
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
{meetingId ? (
<Text style={{ fontSize: 18, padding: 12 }}>
Meeting Id :{meetingId}
</Text>
) : null}
<ParticipantList />
<ControlsContainer
join={join}
leave={leave}
toggleWebcam={toggleWebcam}
toggleMic={toggleMic}
/>
</View>
);
}
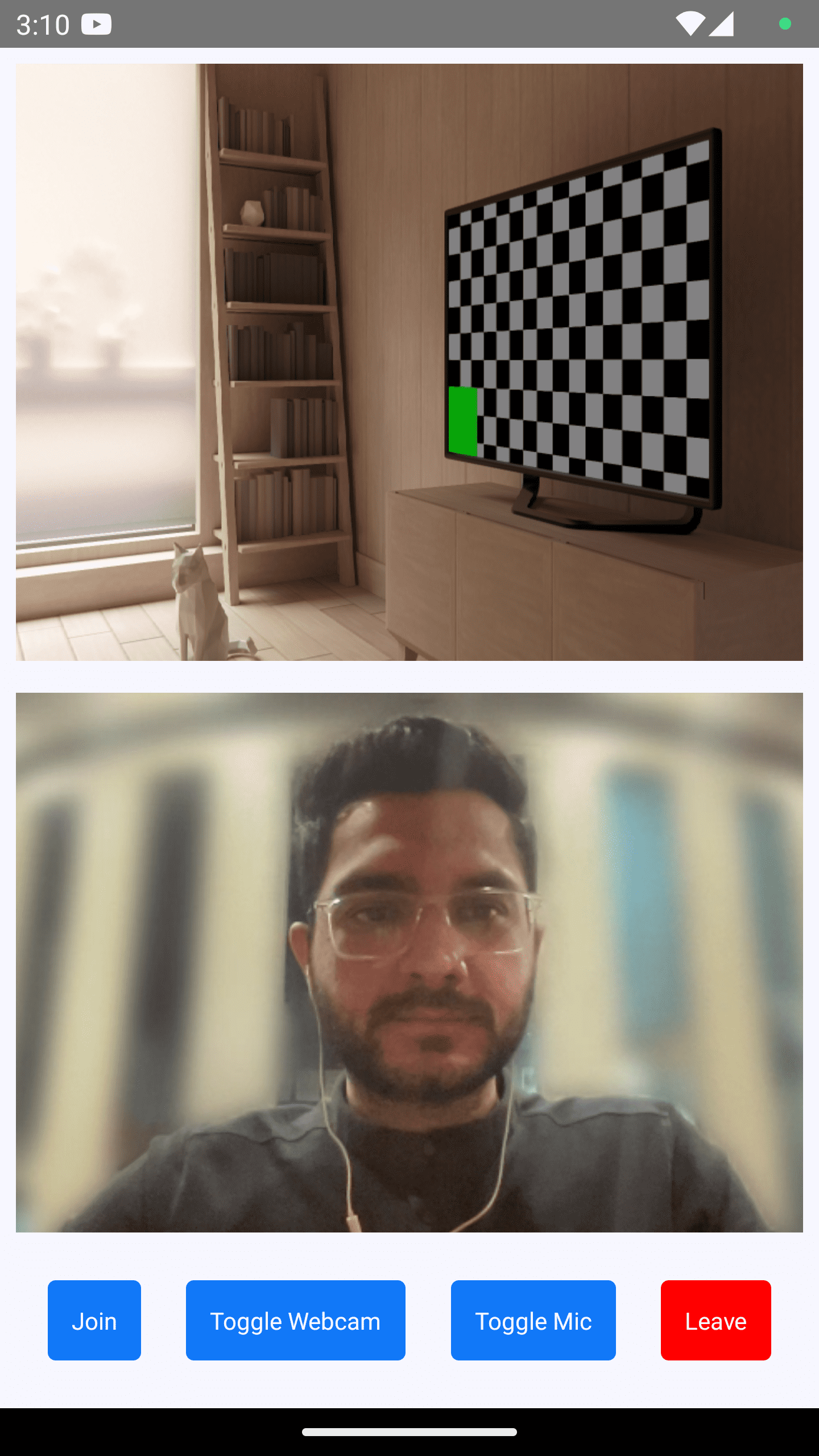
Output

Step 5 : Render Participant List
After implementing controls, now it's time to render joined participants.
We will get joined participants from useMeeting Hook.
function ParticipantView() {
return null;
}
function ParticipantList({ participants }) {
return participants.length > 0 ? (
<FlatList
data={participants}
renderItem={({ item }) => {
return <ParticipantView participantId={item} />;
}}
/>
) : (
<View
style={{
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: "#F6F6FF",
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<Text style={{ fontSize: 20 }}>Press Join button to enter meeting.</Text>
</View>
);
}
function MeetingView() {
// Get `participants` from useMeeting Hook
const { join, leave, toggleWebcam, toggleMic, participants } = useMeeting({});
const participantsArrId = [...participants.keys()];
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<ParticipantList participants={participantsArrId} />
<ControlsContainer
join={join}
leave={leave}
toggleWebcam={toggleWebcam}
toggleMic={toggleMic}
/>
</View>
);
}
Step 6 : Handling Participant Media
Before Handling Participant Media, We need to understand couple of concepts.
1. useParticipant Hook
useParticipant hook is responsible to handle all the properties and events of one particular participant joined in the meeting. It will take participantId as argument.
const { webcamStream, webcamOn, displayName } = useParticipant(participantId);
2. MediaStream API
MediaStream is useful to add MediaTrack to the RTCView component to play the audio and video.
<RTCView
streamURL={new MediaStream([webcamStream.track]).toURL()}
objectFit={"cover"}
style={{
height: 300,
marginVertical: 8,
marginHorizontal: 8,
}}
/>
Rendering Participant Media
function ParticipantView({ participantId }) {
const { webcamStream, webcamOn } = useParticipant(participantId);
return webcamOn && webcamStream ? (
<RTCView
streamURL={new MediaStream([webcamStream.track]).toURL()}
objectFit={"cover"}
style={{
height: 300,
marginVertical: 8,
marginHorizontal: 8,
}}
/>
) : (
<View
style={{
backgroundColor: "grey",
height: 300,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
}}
>
<Text style={{ fontSize: 16 }}>NO MEDIA</Text>
</View>
);
}
Output

Stuck anywhere? Check out this example code on GitHub.
Expo user, you can refer this example code on GitHub.
Run your application
npm run android // Android
npm run ios // iOS
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

