Scalability Guide for Large Participant Meetings
Overview
Hosting video meetings with 10+ participants can be challenging, but don’t worry—we’ve got you covered! This guide will walk you through two powerful features that can transform your large meetings into smooth, efficient experiences:
- Player Component: Automatically pauses off-screen video streams to save bandwidth.
- Adaptive Subscriptions: Smartly prioritizes audio and video streams based on who’s speaking.
These tools tackle common issues like excessive bandwidth usage and poor quality for users with limited networks. Let’s dive in and see how they can make your meetings better!
Pro Tip: These features are flexible—you can use them together or separately. For example, you can implement Adaptive Subscriptions with your existing player setup or use the Player Component on its own.
Common Challenges in Large Meetings
1. Excessive Bandwidth Consumption
The Problem: All video streams stay active, even when they’re not visible on the screen.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
- Users with limited bandwidth struggle with high data usage.
- Call quality and performance take a hit.
- Resources are wasted on streams no one is watching.
2. Ineffective Stream Prioritization
The Problem: All streams are treated equally, even when some are more important than others.
Why It’s a Big Deal:
- Users with poor networks experience low-quality streams.
- Audio clarity suffers when competing with video for bandwidth.
- Key speakers might not be seen or heard clearly.
Solution Features
Player Component
The Player Component is like a smart assistant for your video streams—it knows when to pause and resume streams based on what’s visible on the screen.
Why You’ll Love It:
- Automatically detects which streams are visible.
- Pauses streams for participants who are off-screen.
- Reduces bandwidth usage significantly.
- Adjusts stream quality to fit the container size with
maxQuality: "auto".
How It Works:
Imagine scrolling through a list of participants. The Player Component pauses streams that are out of view and resumes them when they come back into view. It’s seamless and efficient!
Visual Illustration:
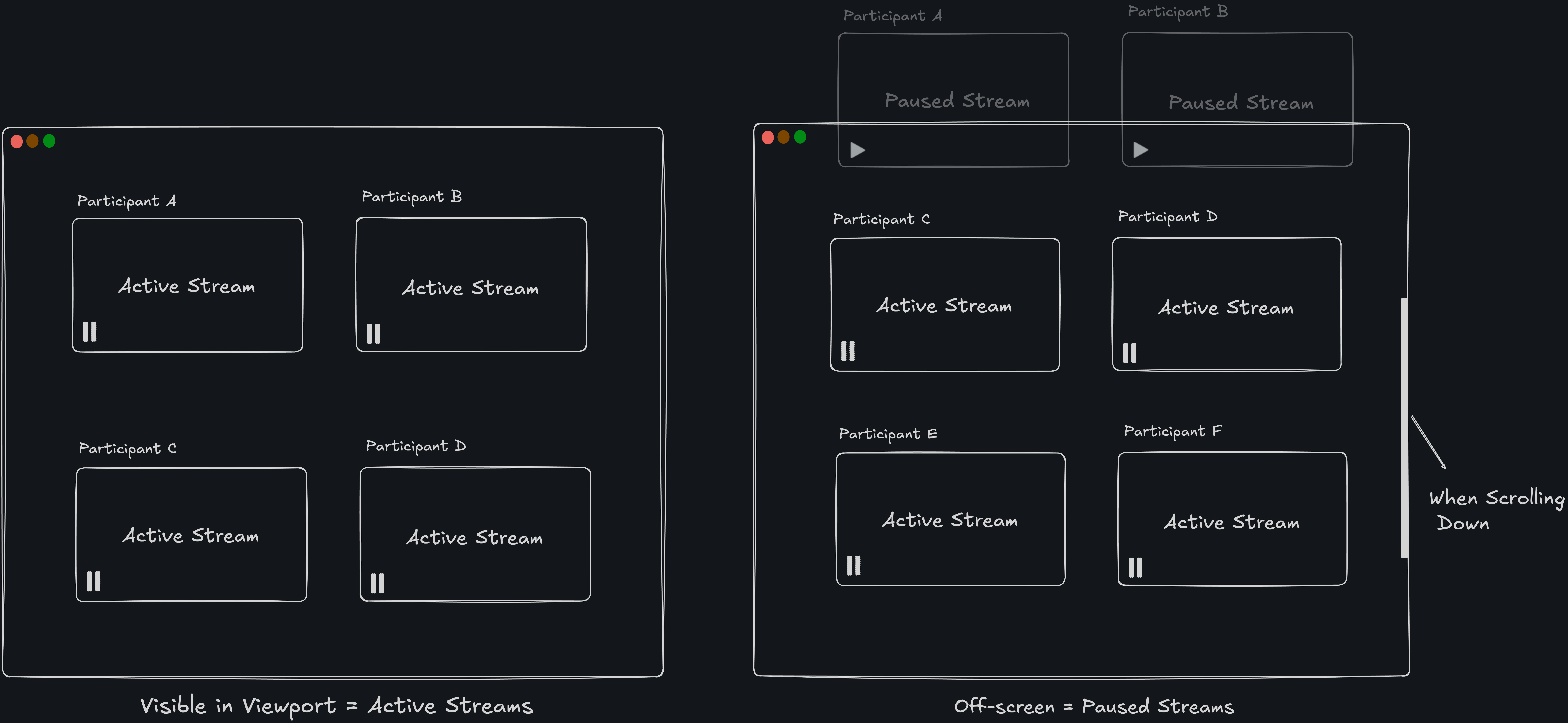
Quality Adaptation Example:
Let’s say a participant’s original video is 720p, but your container size is 320x180. With maxQuality: "auto", the player will only consume a 320p stream, saving bandwidth without compromising quality.
Adaptive Subscriptions
Adaptive Subscriptions take the guesswork out of stream prioritization. They focus on what matters most—active speakers and pinned participants.
Why You’ll Love It:
- Automatically identifies and prioritizes dominant speakers.
- Manages bandwidth intelligently for users with constraints.
- Ensures crystal-clear audio, even on weak networks.
- Keeps pinned participants at the highest quality.
How It Works:
The system analyzes who’s speaking and adjusts stream priorities accordingly. For users with limited bandwidth, it pauses or lowers the quality of less important streams. Pinned participants always get VIP treatment!
Visual Illustration:
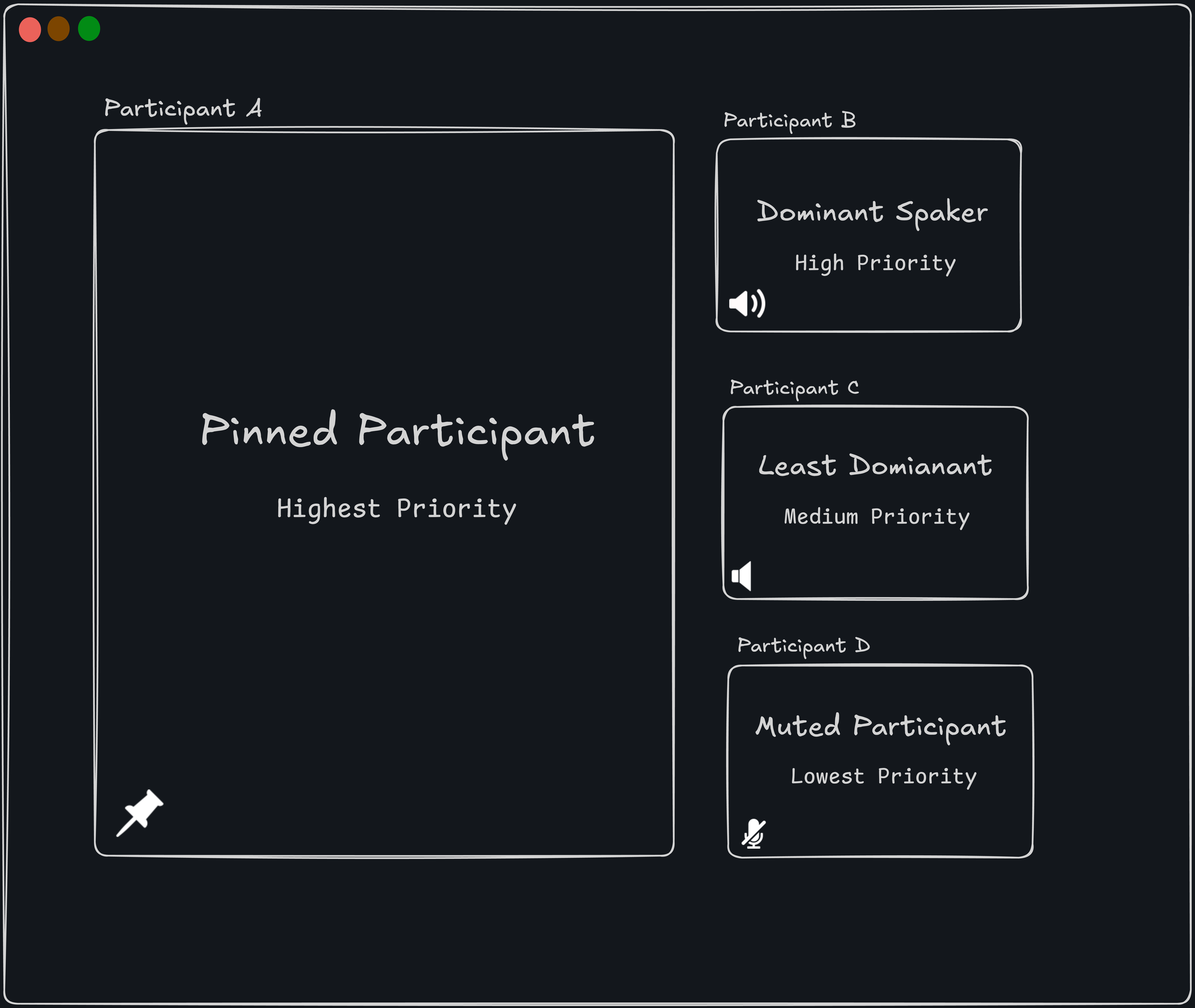
Under Bandwidth Constraints:
- Muted participants’ videos are paused first.
- Least dominant speakers are paused next.
- Pinned participants are always maintained at the highest quality.
Want to add pin/unpin functionality? Check out this documentation.
Implementation Guide
Prerequisites
- SDK Version: 0.2.2 or later.
Enabling Adaptive Subscriptions(BETA)
Turning on Adaptive Subscriptions is as easy as flipping a switch:
const { enableAdaptiveSubscriptions, disableAdaptiveSubscriptions } =
useMeeting();
// Enable adaptive subscriptions
enableAdaptiveSubscriptions();
// Disable adaptive subscriptions
disableAdaptiveSubscriptions();
Recommended Implementation:
// Enable on meeting join
const { join, participants, enableAdaptiveSubscriptions } = useMeeting({
// Callback for when the meeting is joined successfully
onMeetingJoined: () => {
enableAdaptiveSubscriptions();
},
});
Stream Pause/Resume Events
Stay informed when streams are paused or resumed with these event listeners:
useParticipant("participantId", {
onStreamPaused: ({ kind, reason }) => {
console.log(reason); // Possible values: "muted", "leastDominance"
},
onStreamResumed: ({ kind, reason }) => {
console.log(reason); // Possible values: "adaptiveSubscriptionsDisabled", "networkStable"
},
});
Pause Reasons:
muted: The participant has turned off their audio.leastDominance: The participant hasn’t spoken much.
Resume Reasons:
adaptiveSubscriptionDisabled: The feature was disabled.networkStable: Network conditions have improved.
Developer Tip: Add a UI indicator to let users know when a stream is paused, like “Paused due to weak network.”
Rendering Video and Audio
Video Rendering
You can render video in two ways: use the default VideoPlayer component or create your own custom player wrapped with the withAdaptiveObservers HOC.
Using VideoPlayers(BETA)
import { VideoPlayer } from "@videosdk.live/react-sdk";
const ParticipantView = ({ participantId }) => {
return (
<VideoPlayer
participantId={participantId} // Required
type="video" // "video" or "share"
containerStyle={{
height: "100%",
width: "100%",
}}
className=""
classNameVideo=""
videoStyle={{}}
/>
);
};
VideoPlayer Parameters:
participantId
Unique participant ID.
- Type:
String— Required
type
Stream type to display (video or share).
- Type:
String— Default:"video" - No observers for
share
containerStyle
Custom styles for the container.
- Type:
Object
className
Extra classes for the container.
- Type:
String
classNameVideo
Extra classes for the <video> tag.
- Type:
String— Required
videoStyle
Custom styles for the <video> tag.
- Type:
Object— Required
Using Custom Players(BETA)
import React, { useMemo } from "react";
import { withAdaptiveObservers } from "@videosdk.live/react-sdk";
// Custom video player component
const CustomVideoPlayer = ({ participantId, type }) => {
return (
<>
{/* Render your custom video player UI here */}
...
</>
);
};
// Wrap CustomVideoPlayer with adaptive observers
const VideoPlayerComponent = useMemo(() => {
return withAdaptiveObservers(CustomVideoPlayer);
}, [type, participantId]);
Custom Player Parameters:
participantId
Unique participant ID.
- Type:
String— Required
type
Stream type to display (video or share).
- Type:
String— Default:"video" - No observers for
share
Important Notes on Quality Settings:
- When using
maxQuality: "auto", the player automatically selects the optimal stream quality based on container dimensions. - If
multiStreamis set to false, themaxQuality: "auto"setting will not work. - When using
maxQuality: "auto", you cannot use thesetQuality()method ofuseParticipanthook. - To manually control quality, use specific values:
maxQuality: "high",maxQuality: "med", ormaxQuality: "low".
Audio Renderings(BETA)
import { AudioPlayer } from "@videosdk.live/react-sdk";
<AudioPlayer
participantId={participantId}
type="audio" // "audio" or "shareAudio"
/>;
AudioPlayer Parameters:
participantId
Unique participant ID.
- Type:
String— Required
type
Stream type to render (audio or shareAudio).
- Type:
String— Default:"audio"
Best Practices
- Enable adaptive subscriptions at the start of every meeting.
- Design your UI to display indicators when a stream is paused.
- Pin important participants to ensure they receive the highest streaming priority.
- Consider implementing pagination for very large meetings to further reduce resource usage.
- For maximum bandwidth efficiency:
- Use container-appropriate sizes that match your layout needs.
- Enable multiStream for the auto-quality feature to work.
- Design your UI to show fewer high-quality streams rather than many low-quality ones.
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

