Quick Start for Conference in Android
VideoSDK enables you to embed the video calling feature into your Android application in minutes.
In this quickstart, we are going to explore group calling feature of Video SDK. We will go through step by step guide of integrating video calling with Android Video SDK.
This guide will get you running with the VideoSDK video & audio calling in minutes.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that your development environment meets the following requirements:
- Android Studio Arctic Fox (2020.3.1) or later.
- Android SDK API Level 21 or higher.
- A mobile device that runs Android 5.0 or later.
One should have a VideoSDK account to generate token. Visit VideoSDK dashboard to generate token
Getting Started with the Code!
Follow the steps to create the environment necessary to add video calls into your app. Also you can find the code sample for quickstart here.
Create new Android Project
For a new project in Android Studio, create a Phone and Tablet Android project with an Empty Activity.
After creating the project, Android Studio automatically starts gradle sync. Ensure that the sync succeeds before you continue.
Integrate Video SDK
- Maven Central
- Jitpack
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {url= uri("https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/jcenter")}
}
}
dependencyResolutionManagement{
repositories {
google()
maven { url = uri("https://www.jitpack.io") }
mavenCentral()
maven {url= uri("https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/jcenter")}
}
}
- Add the following dependency in your app's
app/build.gradle.
dependencies {
implementation ("live.videosdk:rtc-android-sdk:0.3.0")
// library to perform Network call to generate a meeting id
implementation ("com.amitshekhar.android:android-networking:1.0.2")
// other app dependencies
}
Android SDK compatible with armeabi-v7a, arm64-v8a, x86_64 architectures. If you want to run the application in an emulator, choose ABI x86_64 when creating a device.
Add permissions into your project
- In
/app/Manifests/AndroidManifest.xml, add the following permissions.
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS"/>
If your project has set android.useAndroidX=true, then set android.enableJetifier=true in the gradle.properties file to migrate your project to AndroidX and avoid duplicate class conflict.
Structure of the project
Your project structure should look like this.
app/
├── src/main/
│ ├── java/com/example/app/
│ │ ├── components/
│ │ ├── screens/
│ │ ├── navigation/
│ │ ├── ui/
│ │ │ └── theme/
│ │ ├── model/
│ │ ├── MainApplication.kt
│ │ ├── MainActivity.kt
│ │ └── NetworkClass.kt
│ ├── res/
│ └── AndroidManifest.xml
├── build.gradle
└── settings.gradle
App Architecture
Step 1: Initialize VideoSDK
- Create
MainApplicationclass which will extend theandroid.app.Application.
- Create field
sampleTokeninMainApplicationwhich will hold the generated token from the VideoSDK dashboard. This token will use in VideoSDK config as well as in generating meetingId.
import android.app.Application
import live.videosdk.rtc.android.VideoSDK
class MainApplication: Application() {
val sampleToken = "YOUR_TOKEN" //paste your token here
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
VideoSDK.initialize(applicationContext)
}
}
- Add
MainApplicationtoAndroidManifest.xml
<application
android:name=".MainApplication" >
<!-- ... -->
</application>
Step 2: Managing Permissions
The MainActivity is the entry point of the application. It handles permission requests for accessing the camera and microphone.
On creation, it checks if the required permissions (RECORD_AUDIO and CAMERA) are granted.
If not, it requests them. Once permissions are granted, it sets the content view using Jetpack Compose and initializes the MyApp composable, which contains the app's navigation and UI logic.
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
checkSelfPermission(REQUESTED_PERMISSIONS[0], PERMISSION_REQ_ID)
checkSelfPermission(REQUESTED_PERMISSIONS[1], PERMISSION_REQ_ID)
setContent {
Videosdk_android_compose_quickstartTheme {
MyApp(this)
}
}
}
private fun checkSelfPermission(permission: String, requestCode: Int): Boolean {
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission) !=
PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED
) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,
REQUESTED_PERMISSIONS, requestCode)
return false
}
return true
}
companion object {
private const val PERMISSION_REQ_ID = 22
private val REQUESTED_PERMISSIONS = arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.RECORD_AUDIO,
Manifest.permission.CAMERA
)
}
}
@Composable
fun MyApp(context: Context) {
NavigationGraph(context = context)
}
Step 3: Setting Up Navigation
The NavigationGraph composable manages navigation between the JoinScreen and MeetingScreen using NavController.
@Composable
fun NavigationGraph(navController: NavHostController = rememberNavController(),context: Context) {
NavHost(navController = navController, startDestination = "join_screen") {
composable("join_screen") {
JoinScreen(navController,context)
}
composable("meeting_screen?meetingId={meetingId}") { backStackEntry ->
val meetingId = backStackEntry.arguments?.getString("meetingId")
meetingId?.let {
MeetingScreen(viewModel = MeetingViewModel(),navController, meetingId, context)
}
}
}
}
Step 4: Creating Components
- Before building the individual screens, it's essential to develop reusable composable components that will be used throughout the project.
- Create a
ReusableComponents.ktfile to organize all reusable components for the project, such as buttons, spacers, and customizable text.
@Composable
fun MyAppButton(task: () -> Unit, buttonName: String) {
Button(onClick = task) {
Text(text = buttonName)
}
}
@Composable
fun MySpacer() {
Spacer(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(1.dp)
.background(color = Color.Gray))}
@Composable
fun MyText(text: String, fontSize: TextUnit = 23.sp) {
Text(
text = text,
fontSize = fontSize,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal,
modifier = Modifier.padding(4.dp),
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium.copy(fontSize = 16.sp),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onSurface.copy(alpha = 0.7f)
)}
- Create a
ParticipantVideoView.ktfile that includes two composable functions:ParticipantVideoViewfor rendering individual participant video streams, andParticipantsGridfor displaying a grid of participant videos.
- Here the participant's video is displayed using
VideoView. To know more aboutVideoView, please visit here VideoViewis a custom View. Since Jetpack Compose does not natively support traditionalViewobjects, we need to integrate theVideoViewinto the Compose layout using theAndroidViewwrapper.AndroidView()is a composable that can be used to add Android views inside a @Composable function.
@Composable
fun ParticipantVideoView(
participant: Participant
) {
var isVideoEnabled by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
LaunchedEffect(participant) {
isVideoEnabled = participant.streams.any { (_, stream) ->
stream.kind.equals("video", ignoreCase = true) && stream.track != null
}
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(200.dp)
.background(if (isVideoEnabled) Color.DarkGray else Color.Gray)
) {
AndroidView(
factory = { context ->
VideoView(context).apply {
for ((_, stream) in participant.streams) {
if (stream.kind.equals("video", ignoreCase = true)) {
val videoTrack = stream.track as VideoTrack
addTrack(videoTrack)
isVideoEnabled = true
}
}
}
},
update = { videoView ->
participant.addEventListener(object : ParticipantEventListener() {
override fun onStreamEnabled(stream: Stream) {
if (stream.kind.equals("video", ignoreCase = true)) {
val videoTrack = stream.track as VideoTrack
videoView.addTrack(videoTrack)
isVideoEnabled = true
}
}
override fun onStreamDisabled(stream: Stream) {
if (stream.kind.equals("video", ignoreCase = true)) {
videoView.removeTrack()
isVideoEnabled = false
}
}
})
},
onRelease = { videoView ->
videoView.releaseSurfaceViewRenderer()
},
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()
)
if (!isVideoEnabled) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Color.DarkGray),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Text(
text = "Camera Off",
color = Color.White
)
}
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.BottomCenter)
.fillMaxWidth()
.background(Color(0x99000000))
.padding(4.dp)
) {
Text(
text = participant.displayName,
color = Color.White,
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)
)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun ParticipantsGrid(
participants: List<Participant>,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
LazyVerticalGrid(
columns = GridCells.Fixed(2),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp),
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(8.dp)
) {
items(participants.size) { index ->
ParticipantVideoView(
participant = participants[index],
)
}
}
}
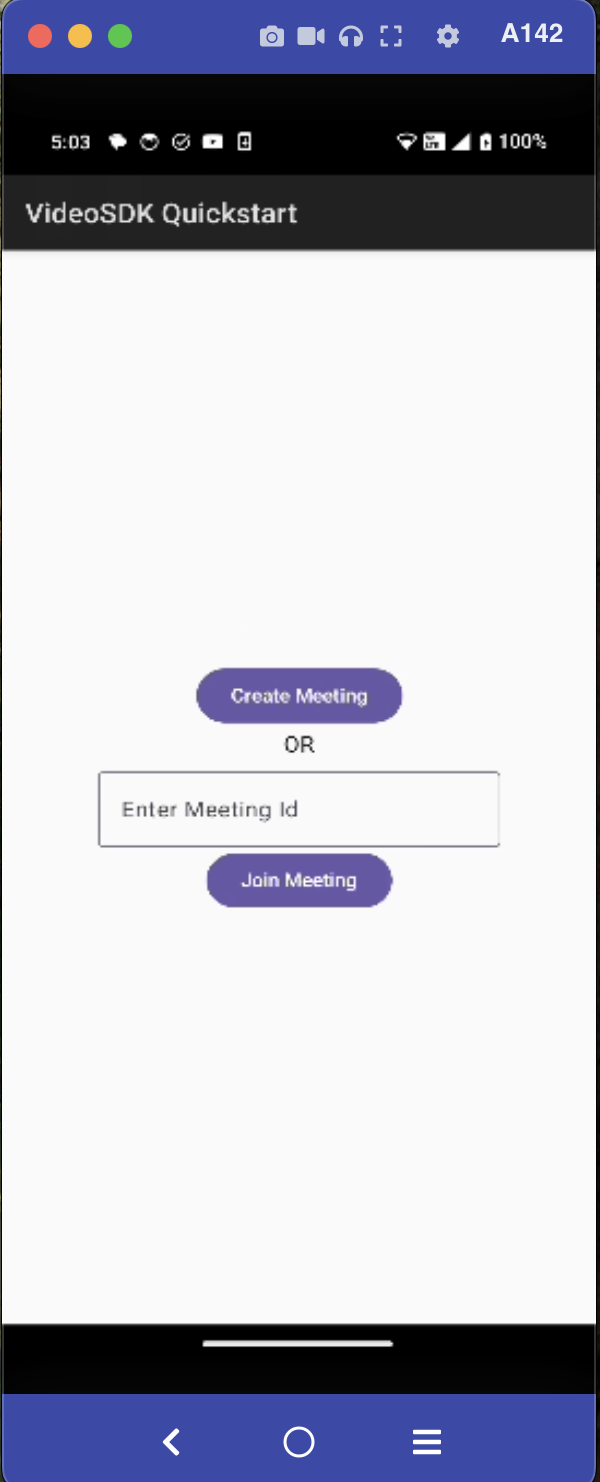
Step 5: Creating Joining Screen
We will create a simple Join screen UI that supports two primary roles:
- Create Meeting: Starts a new meeting.
- Join Meeting: Enter a Meeting ID to join an existing meeting.
The Joining screen will include :
- Create Button - This button will create a new meeting for you.
- TextField for Meeting Id - This text field will contain the meeting Id you want to join.
- Join Button - This button will join the meeting with
meetingIdyou provided.
@Composable
fun JoinScreen(
navController: NavController, context: Context
) {
val app = context.applicationContext as MainApplication
val token = app.sampleToken
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(8.dp),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(4.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceEvenly
) {
var input by rememberSaveable { mutableStateOf("") }
CreateMeetingBtn(navController, token)
Text(text = "OR")
InputMeetingId(input) { updateInput ->
input = updateInput
}
JoinMeetingBtn(navController, input)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun CreateMeetingBtn(navController: NavController, token: String) {
MyAppButton({
NetworkManager.createMeetingId(token) { meetingId ->
navController.navigate("meeting_screen?meetingId=$meetingId")
}
}, "Create Meeting")
}
@Composable
fun InputMeetingId(input: String, onInputChange: (String) -> Unit) {
OutlinedTextField(value = input,
onValueChange = onInputChange,
label = { Text(text = "Enter Meeting Id") })
}
@Composable
fun JoinMeetingBtn(navController: NavController, meetingId: String) {
MyAppButton({
if (meetingId.isNotEmpty()) {
navController.navigate("meeting_screen?meetingId=$meetingId")
}
}, "Join Meeting")
}
Output
Step 6: Creating MeetingId
The NetworkManager singleton handles meeting creation by making a POST request to the VideoSDK API:
- Meeting Creation: Sends a request to the API with an authorization token to create a meeting.
- Response Handling: Extracts the roomId from the response and triggers the
onMeetingCreatedcallback.
object NetworkManager {
fun createMeetingId(token: String, onMeetingIdCreated: (String) -> Unit) {
AndroidNetworking.post("https://api.videosdk.live/v2/rooms")
.addHeaders("Authorization", token)
.build()
.getAsJSONObject(object : JSONObjectRequestListener {
override fun onResponse(response: JSONObject) {
try {
val meetingId = response.getString("roomId")
onMeetingIdCreated(meetingId)
} catch (e: JSONException) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
override fun onError(anError: ANError) {
anError.printStackTrace()
Log.d("TAG", "onError: $anError")
}
})
}
}
Don't confuse with Room and Meeting keyword, both are same thing 😃
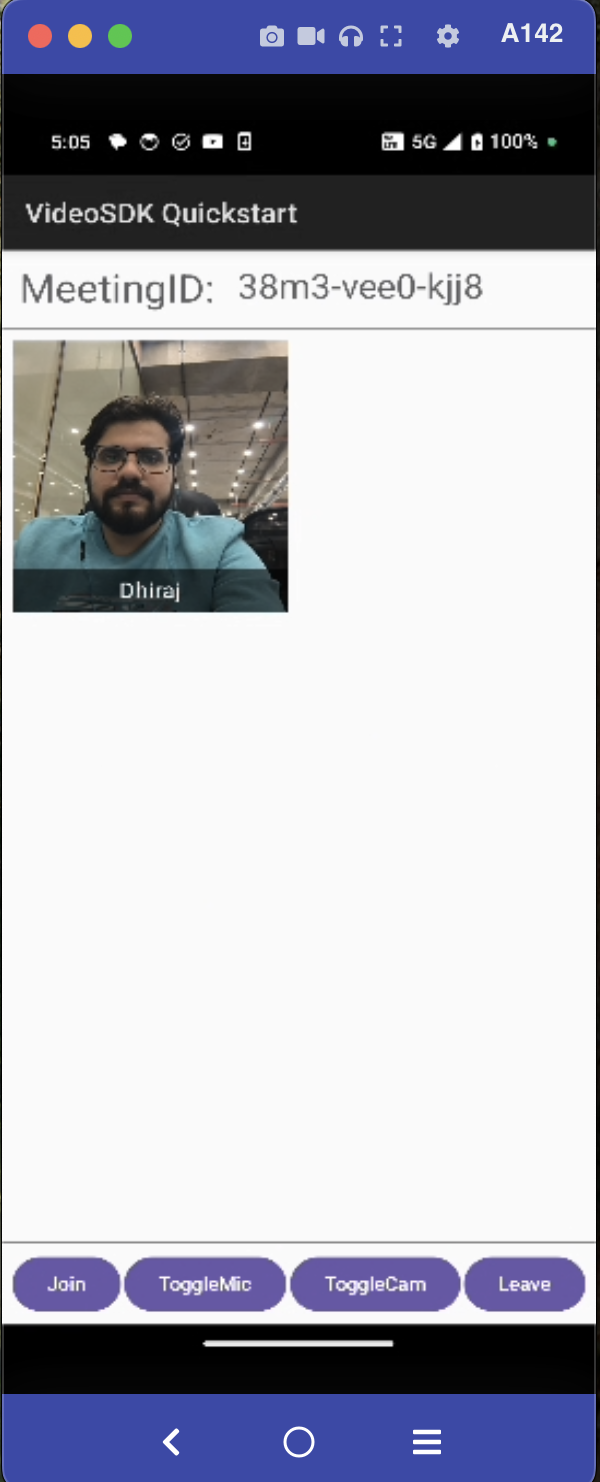
Step 7: Creating Meeting Screen
We will create a simple Meeting screen UI with two main sections:
- Participants' Video Streams: Displays video feeds of meeting participants.
- Media Control Buttons: Includes buttons to control the mic, camera, and leave the meeting.
The MeetingScreen composable is the main UI for a video call meeting, handling meeting details and user actions. The MeetingScreen composable is organized into three sections, each serving a specific purpose:
Header: Displays the meeting ID at the top of the screen for reference.ParticipantsGrid: Shows the list of participants in a grid layout, adjusting dynamically.MediaControlButtons: A set of buttons to control the microphone, camera, and leave the meeting.
@Composable
fun MeetingScreen(viewModel: MeetingViewModel, navController: NavController, meetingId: String, context: Context) {
val app = context.applicationContext as MainApplication
val isMeetingLeft = viewModel.isMeetingLeft
LaunchedEffect(isMeetingLeft) {
if (isMeetingLeft) {
navController.navigate("join_screen")
}
}
Column(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
Header(meetingId)
MySpacer()
ParticipantsGrid(viewModel.participants, Modifier.weight(1f))
MySpacer()
MediaControlButtons(
onJoinClick = {
viewModel.initMeeting(context, app.sampleToken, meetingId)
},
onMicClick = { viewModel.toggleMic() },
onCamClick = { viewModel.toggleWebcam() },
onLeaveClick = {
viewModel.leaveMeeting()
}
)
}
}
@Composable
fun Header(meetingId: String) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(8.dp),
contentAlignment = Alignment.TopStart
) {
Row {
MyText("MeetingID: ", 28.sp)
MyText(meetingId, 25.sp)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun MediaControlButtons(onJoinClick:()->Unit,onMicClick: () -> Unit, onCamClick: () -> Unit, onLeaveClick: () -> Unit) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(6.dp),
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceAround
) {
MyAppButton(onJoinClick,"Join")
MyAppButton(onMicClick,"ToggleMic")
MyAppButton(onCamClick,"ToggleCam")
MyAppButton(onLeaveClick,"Leave")
}
}
Step 8: Setting Up MeetingViewModel
The MeetingViewModel manages the meeting state, handles participants, and controls microphone and camera settings to ensure a smooth video call experience.
Managing Meeting State and Media Control:
- Meeting Initialization: Initializes the meeting with the VideoSDK and adds an event listener.
- Participant Management: Tracks participants, adding/removing them as they join/leave.
- Media Control: Toggles microphone and webcam states.
- Leave Meeting: Allows users to leave the meeting.
class MeetingViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var meeting: Meeting? = null
private var micEnabled by mutableStateOf(true)
private var webcamEnabled by mutableStateOf(true)
val participants = mutableStateListOf<Participant>()
//used in MeetingScreen to handle navigation
var isMeetingLeft by mutableStateOf(false)
private set
fun initMeeting(context: Context, token: String, meetingId: String ) {
VideoSDK.config(token)
if(meeting==null){
meeting = VideoSDK.initMeeting(
context, meetingId, "John Doe",
micEnabled, webcamEnabled, null, null, true, null, null)
}
meeting!!.addEventListener(meetingEventListener)
meeting!!.join()
}
private val meetingEventListener: MeetingEventListener = object : MeetingEventListener() {
override fun onMeetingJoined() {
Log.d("#meeting", "onMeetingJoined()")
meeting?.let { participants.add(it.localParticipant) }
}
override fun onMeetingLeft() {
Log.d("#meeting", "onMeetingLeft()")
meeting = null
isMeetingLeft = true
}
override fun onParticipantJoined(participant: Participant) {
participants.add(participant)
}
override fun onParticipantLeft(participant: Participant) {
participants.remove(participant)
}
}
fun toggleMic() {
if (micEnabled) {
meeting?.muteMic()
} else {
meeting?.unmuteMic()
}
micEnabled = !micEnabled
}
fun toggleWebcam() {
if (webcamEnabled) {
meeting?.disableWebcam()
} else {
meeting?.enableWebcam()
}
webcamEnabled = !webcamEnabled
}
fun leaveMeeting() {
meeting?.leave()
}
}
Final Output
We are done with implementation of customised video calling app in Android using Video SDK. To explore more features go through Basic and Advanced features.
You can checkout the complete quick start example here.
Got a Question? Ask us on discord

